What is ANR?
Ambiguous Name Resolution (ANR) is an efficient search algorithm associated with Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) clients that allows for objects to be bound without complex search filters. ANR is useful when you are locating objects and attributes that may or may not be known by the client. A common use for ANR, for example, is in a situation in which a building name is known by the requesting client, but not the associated number. In this case, the physicalDeliveryOfficeName attribute may have a value of “Building 40” and a client might search for “Building.” ANR returns a match in this instance. It also returns other matches containing the word “Building.”
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/243299/en-us
By default ANR uses these attributes to search within:
- GivenName
- Surname
- displayName
- LegacyExchangeDN
- msExchMailNickname
- RDN
- physicalDeliveryOfficeName
- proxyAddress
- sAMAccountName
Example
Search for users with Smith or Johnson in at least one of the attributes mentioned above.
(&(objectCategory=person)(objectClass=user)(|(anr=Smith)(anr=Johnson)))
Add attributes to ANR
You can include many more attributes to ANR than those mentioned above. To do so you’ll need to edit the Active Directory Schema. This requires to be a member of the Schema Admins Active Directory group and to have the Active Directory Schema MMC Snap-In registered (regsvr32 schmmgmt.dll).
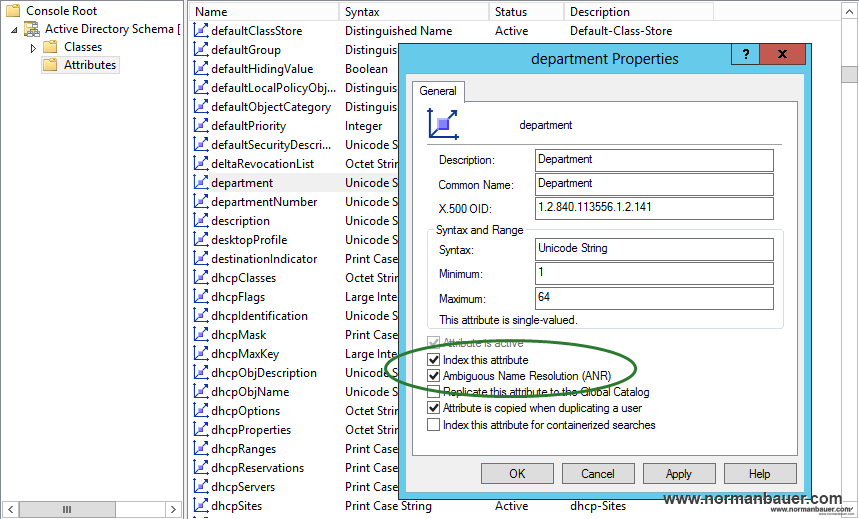
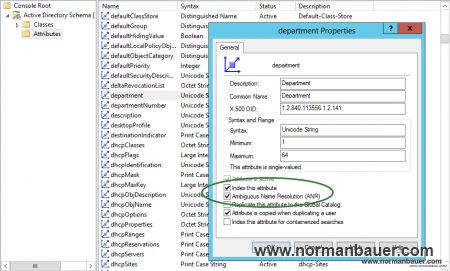
To add a particular attribute (for example Department) navigate to Attributes -> department and open the properties dialog. Check “Index this attribute” and “Ambigous Name Resolution (ANR)”. Hit apply and you are all done.



Recent Comments